Menu
Anatomy Of African Violet Flowers And Leaves
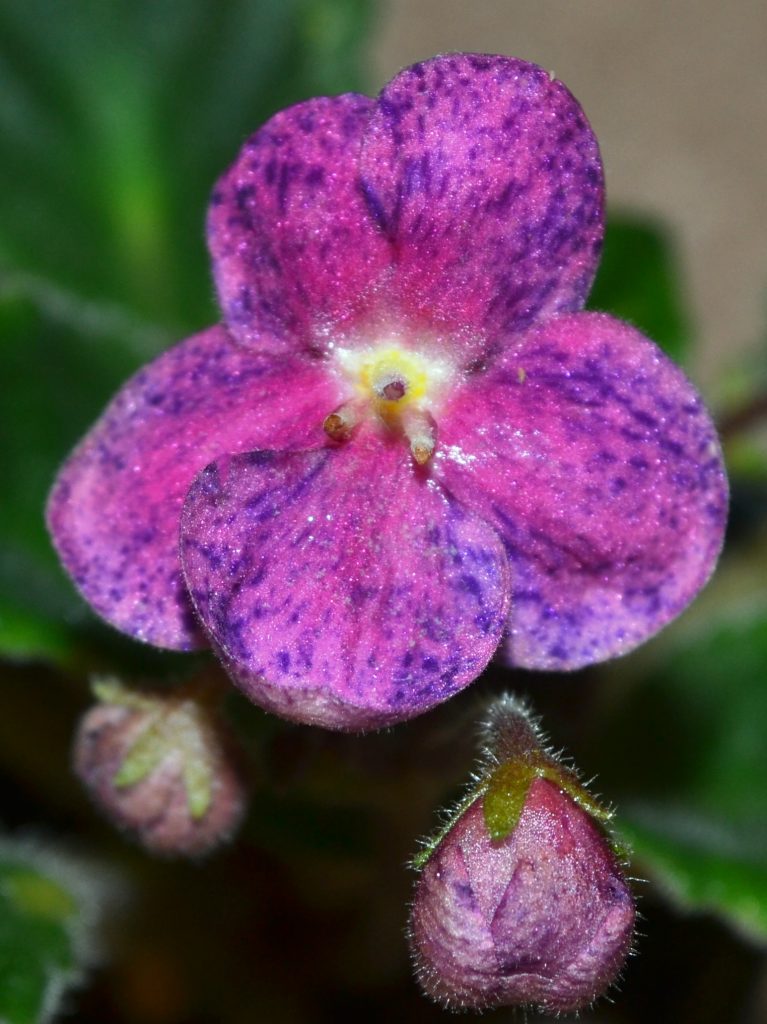
African Violet Flowers:
- African Violet flowers can be of different shapes. These include single, double, semi-double, frilled, fluted, star, wasp and cup shaped flowers. For more details on each flower shape, can visit my blog post, “What are the Different Shapes of African Violet Flowers?”
- African Violet flowers can also be of different color patterns. These include two-tone, bi-color, multi-color, Geneva, dark eye etc… For more details on each flower color pattern, can visit my blog post, “What are the Different Color Patterns of African Violet Flowers?”
- However, the basic structure of all African Violet flowers remains the same.
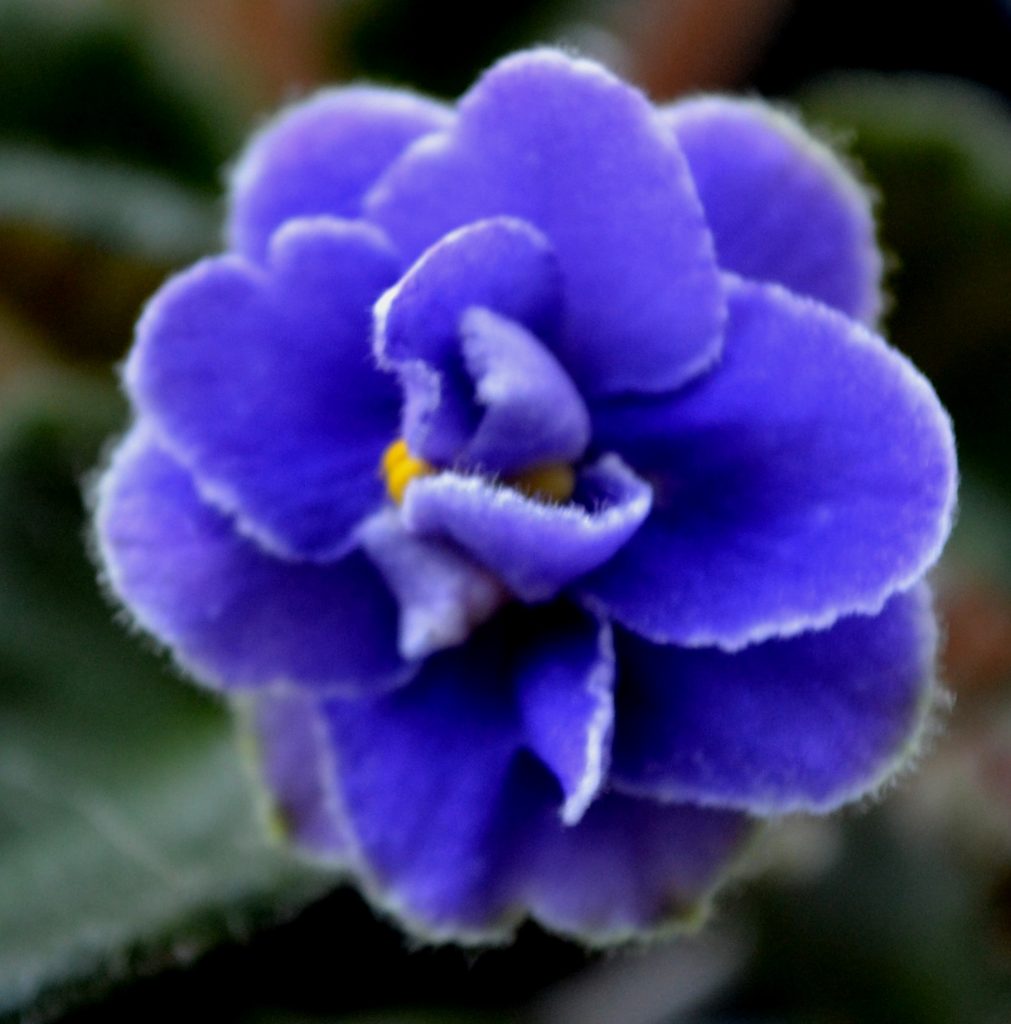
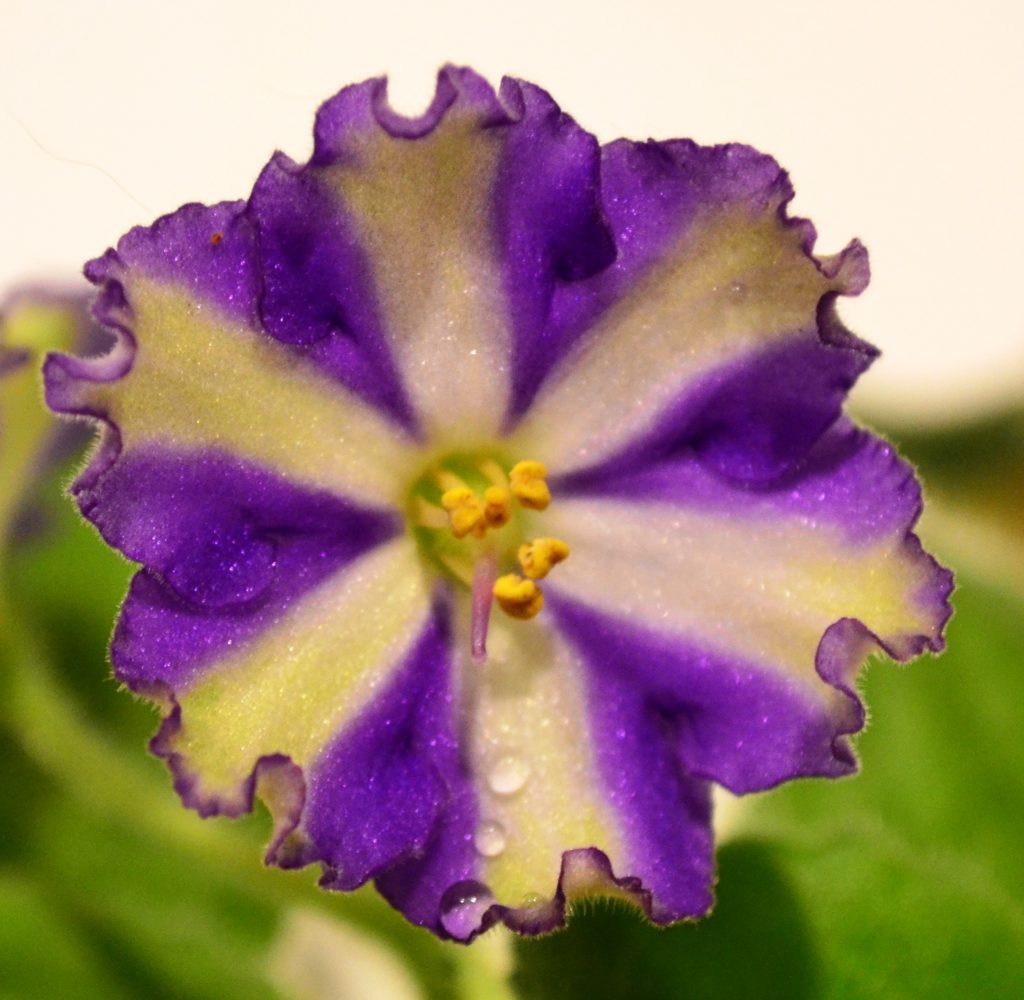
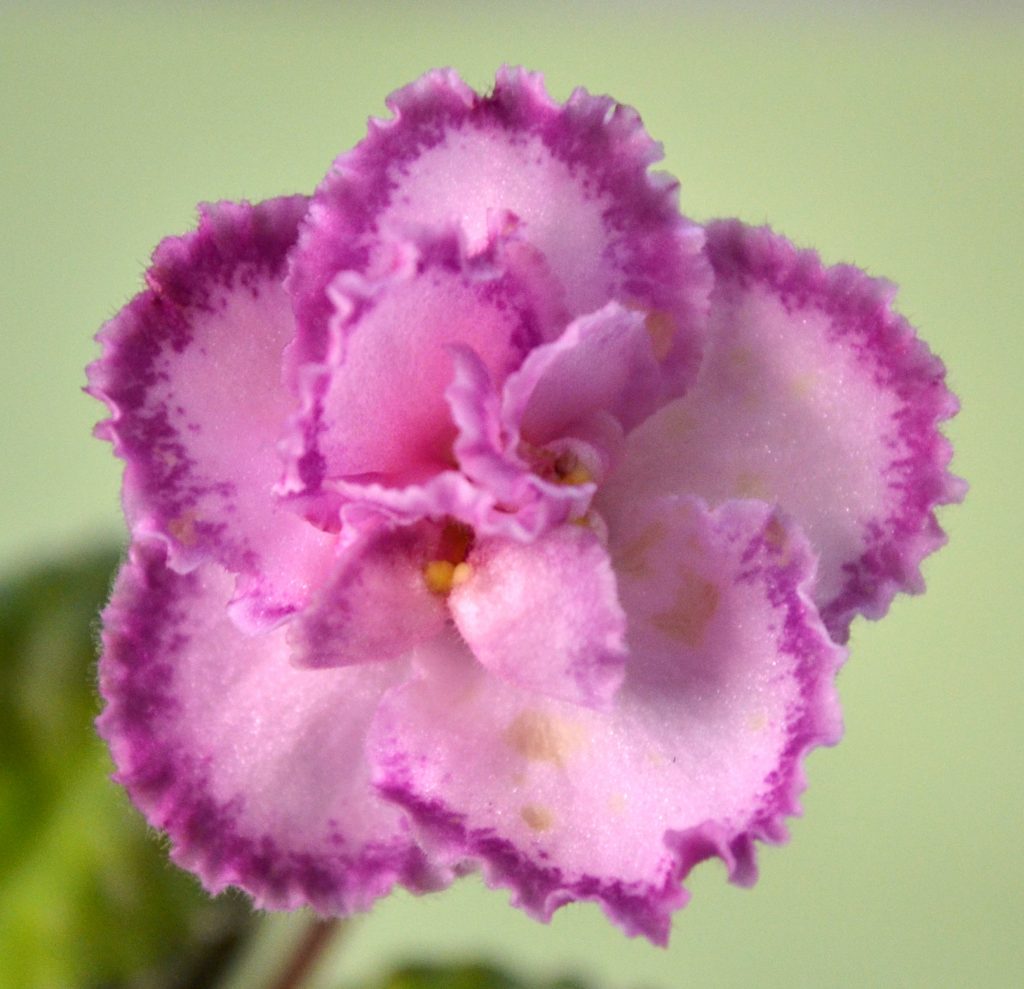
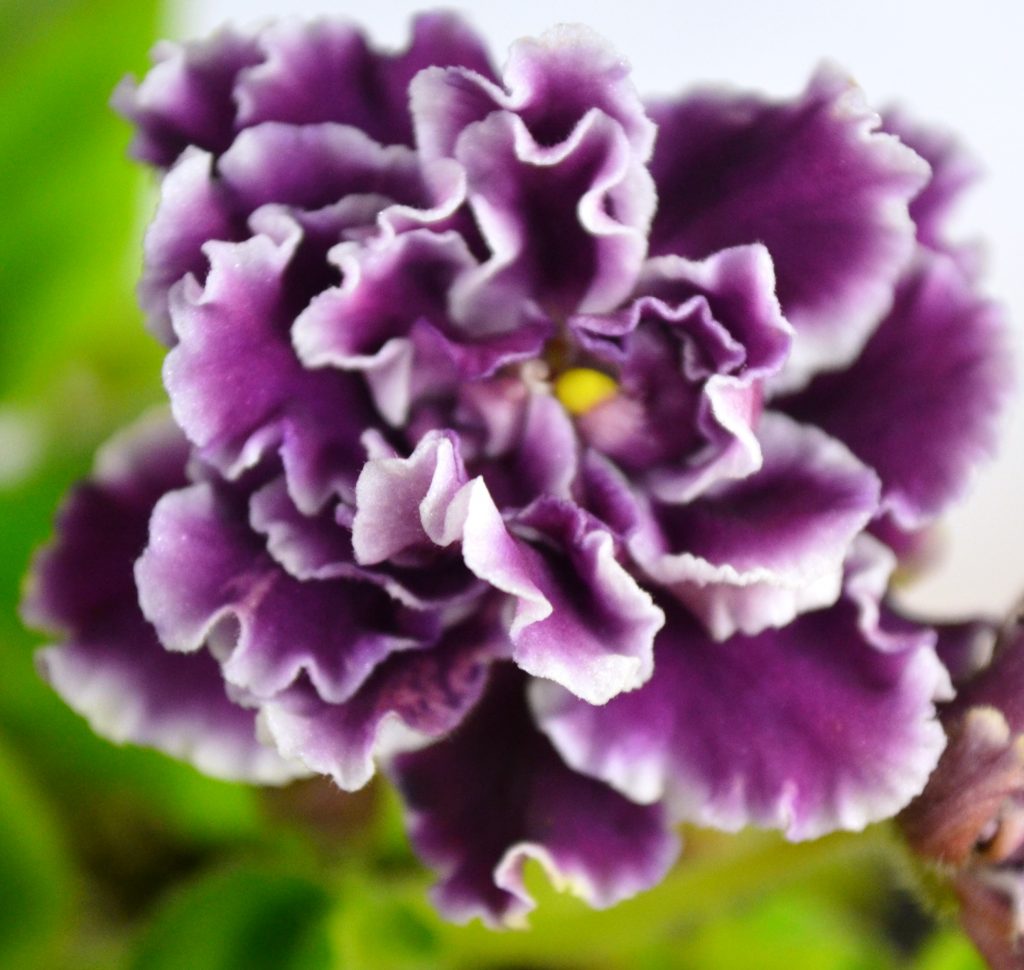
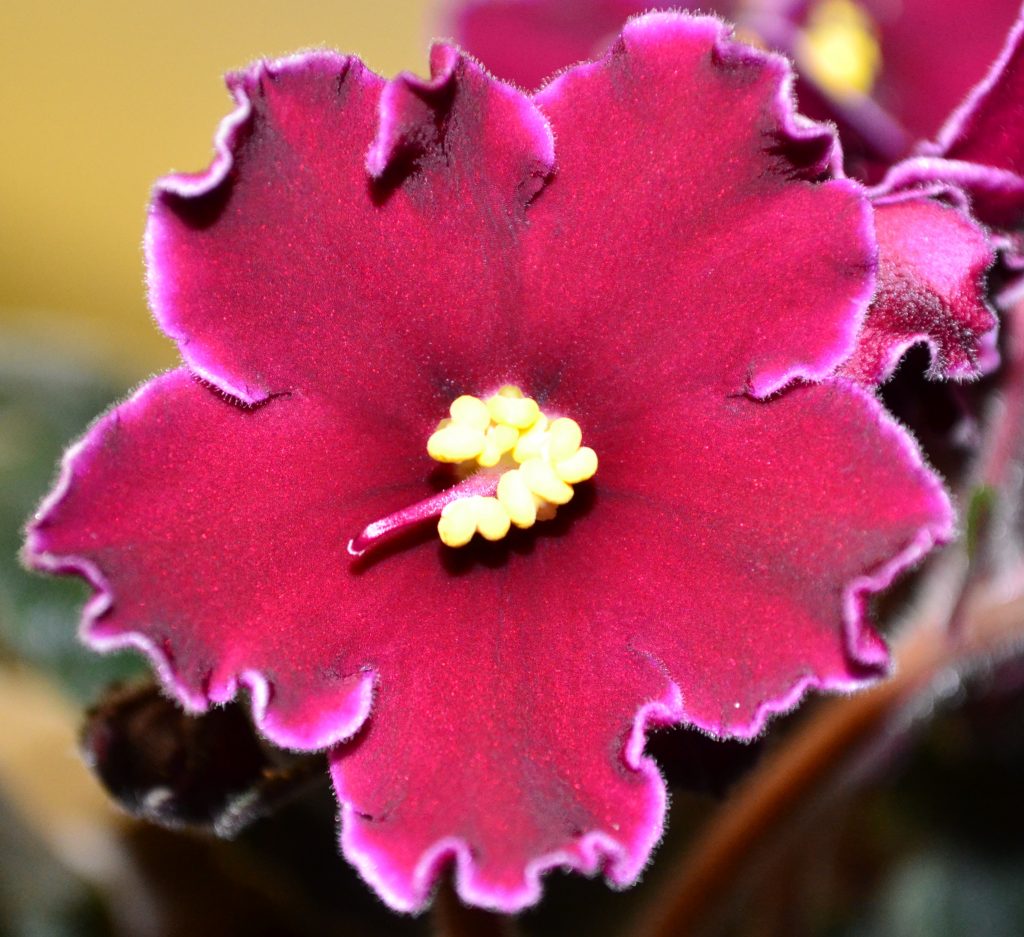






Parts of an African Violet Flower:
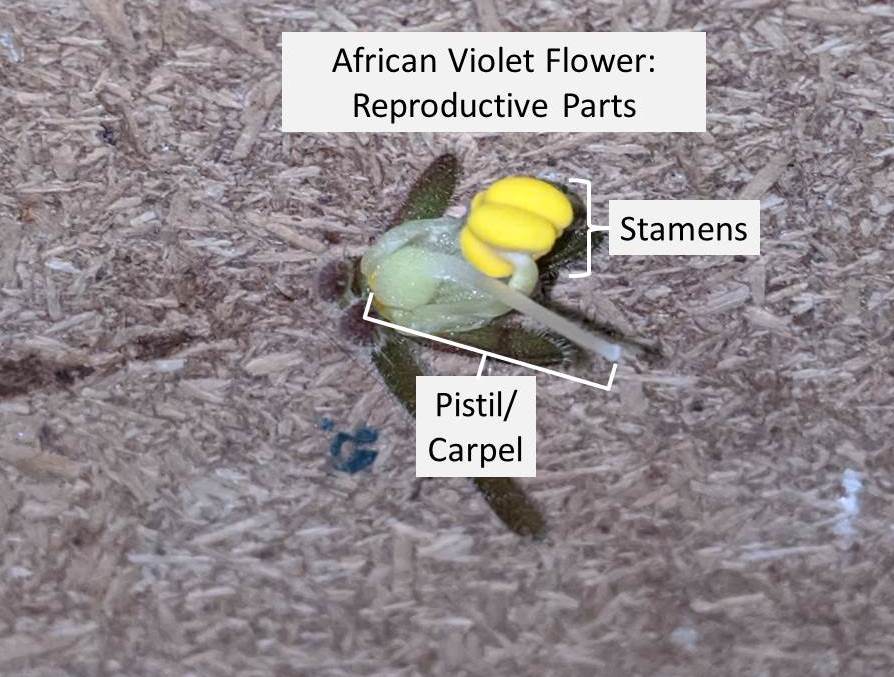
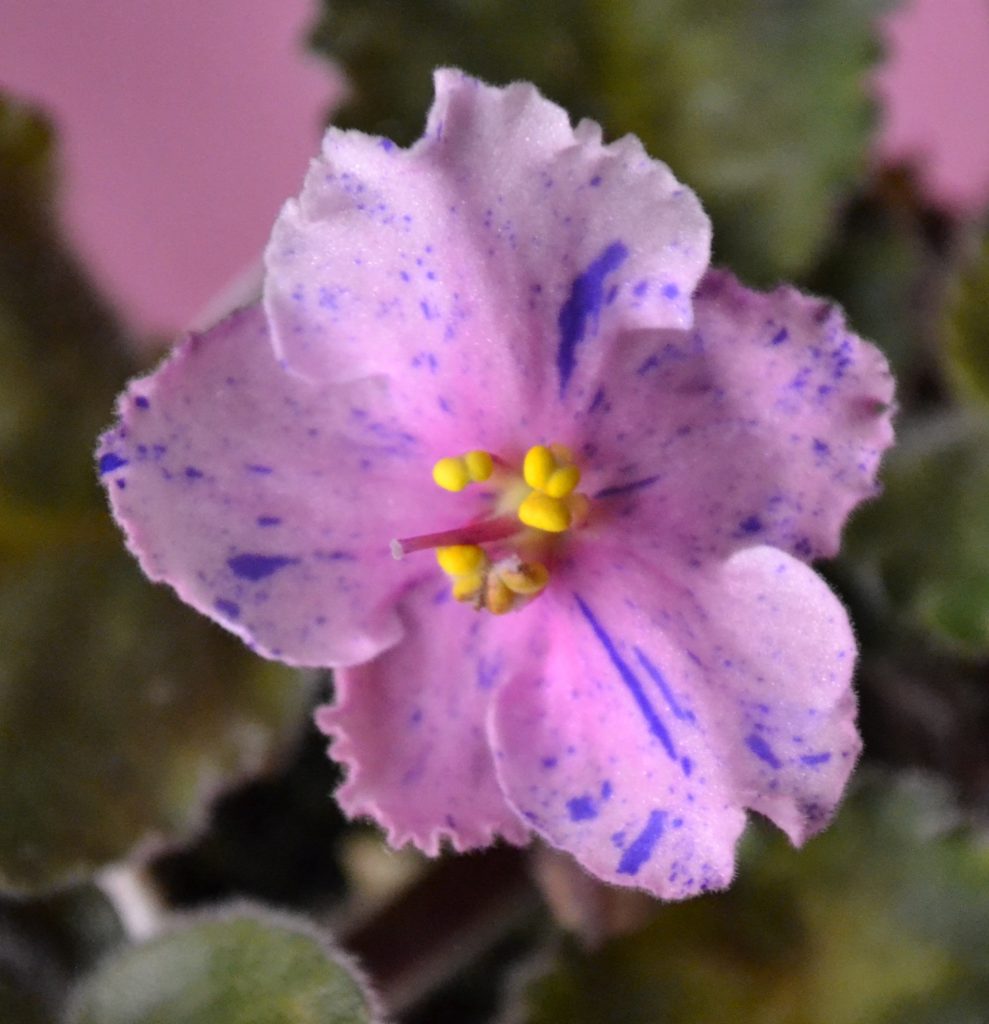
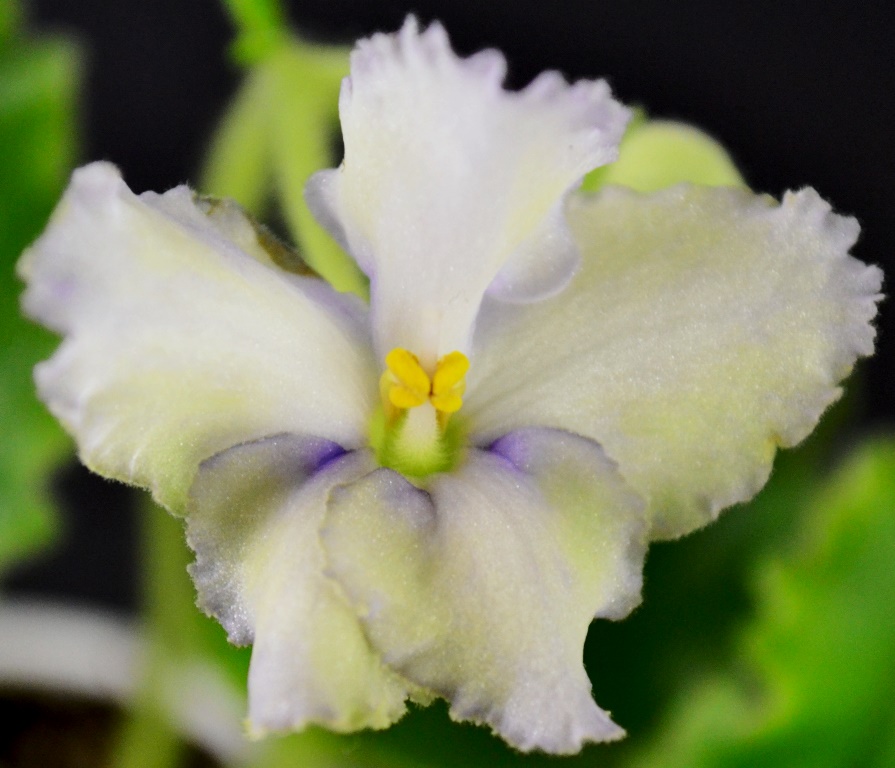
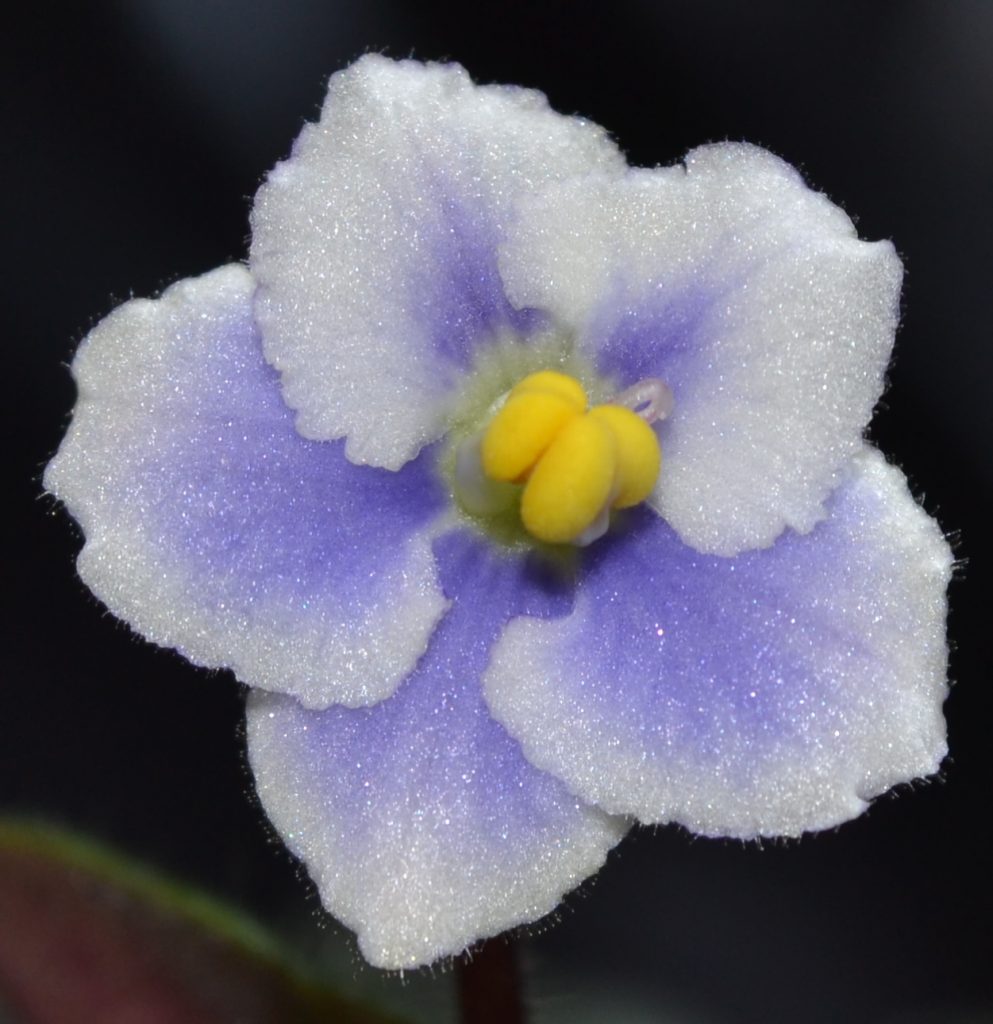
- There are four basic parts of an African Violet Flower, these include petal, stamen, pistil and stem. These are shown in the diagram below:
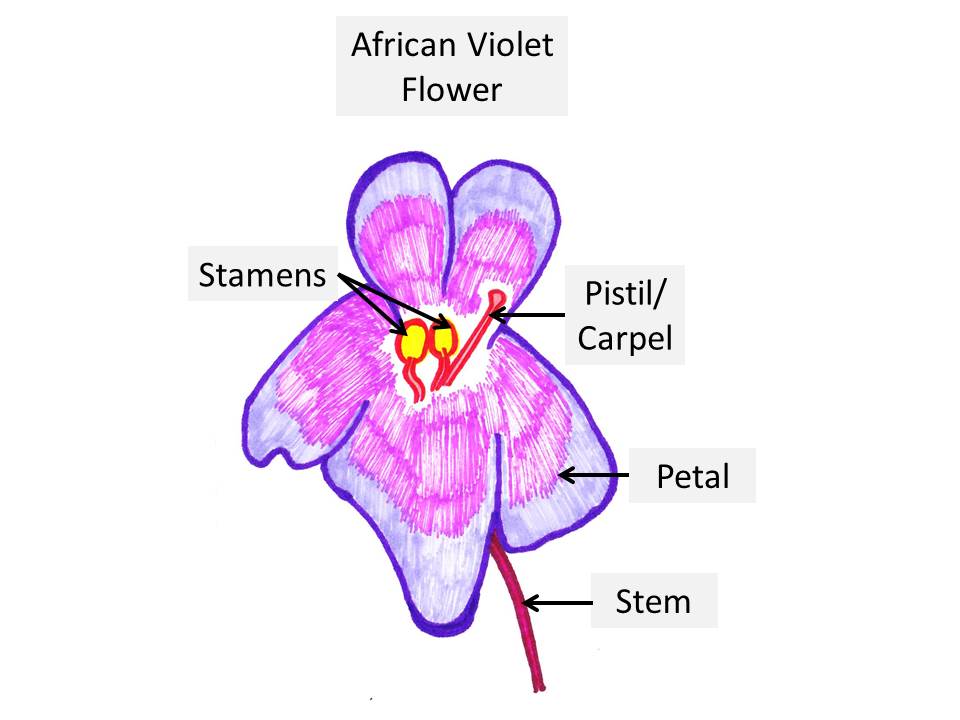
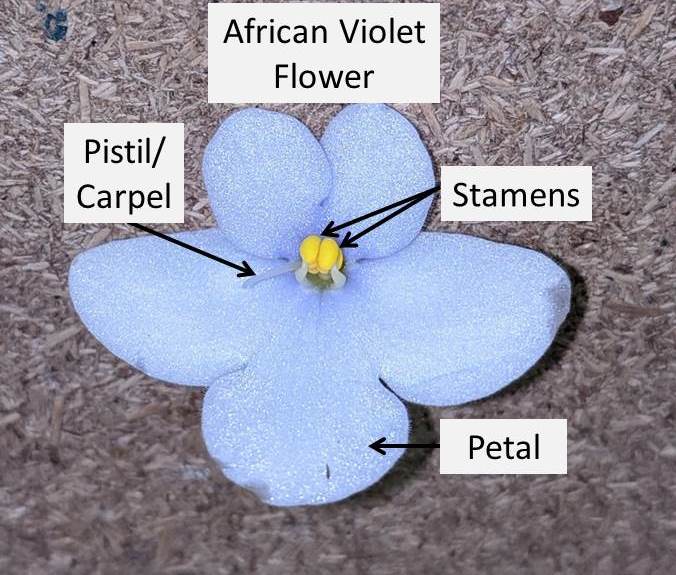

- Petals:
- The petal or petals are modified leaves and form colorful parts of the flower.
- Petals together are known as corolla of the flower and each individual petal is known as lobe of the flower.
- The function of petals is to form a surrounding around the reproductive parts of a flower.
- An African Violet flower, can contain petals of different shapes.
- On an African Violet plant, a single flower can contain anywhere from 5-10 petals, depending upon the type of flower it is.






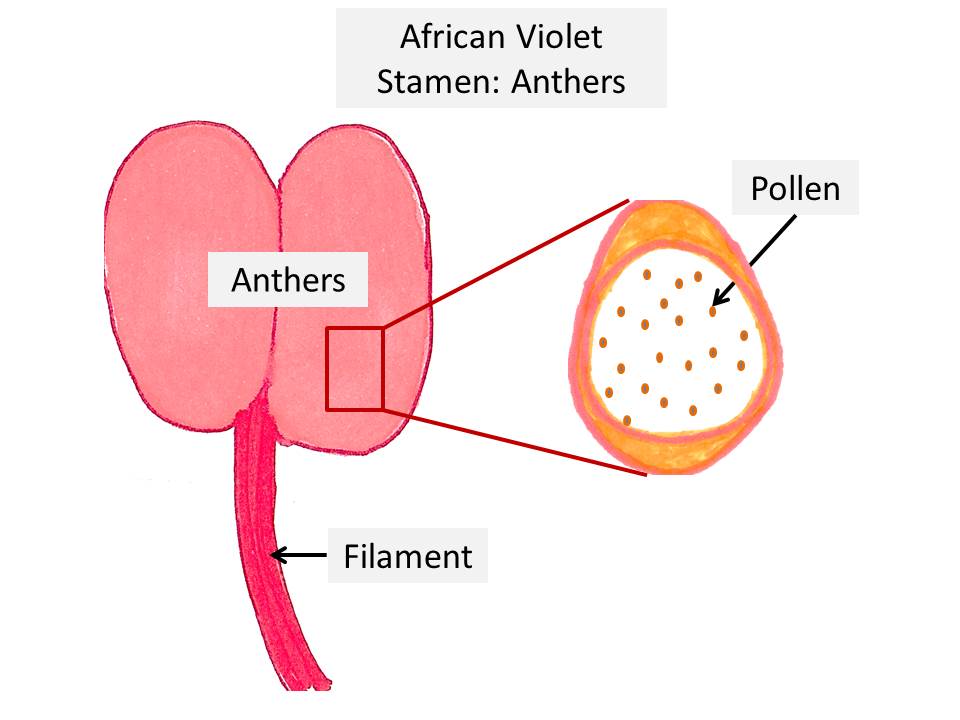
2. Stamen:
- Stamen is the male reproductive part of the flower.
- Stamen is made up of two parts the anther and the filament
- Within the stamen, anther is at the top and filament at the bottom, holding the anther in place.
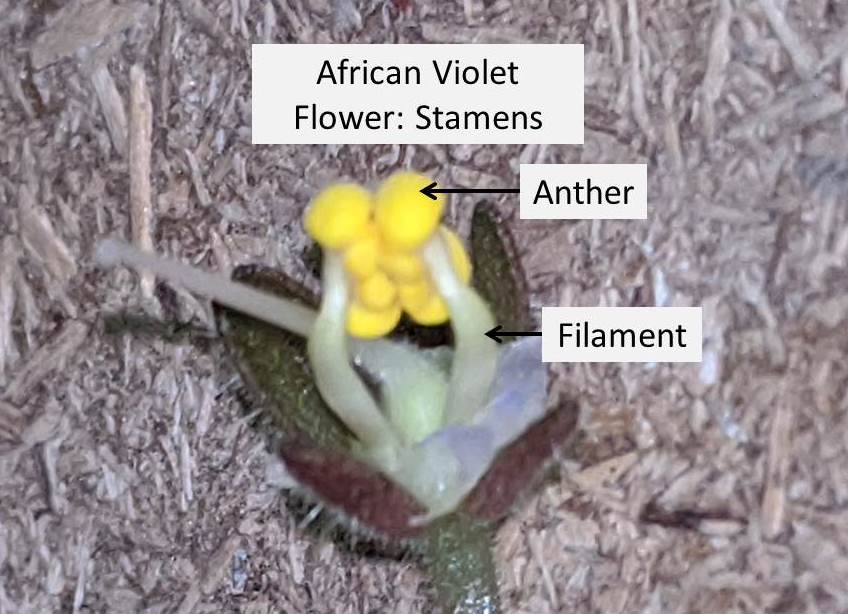

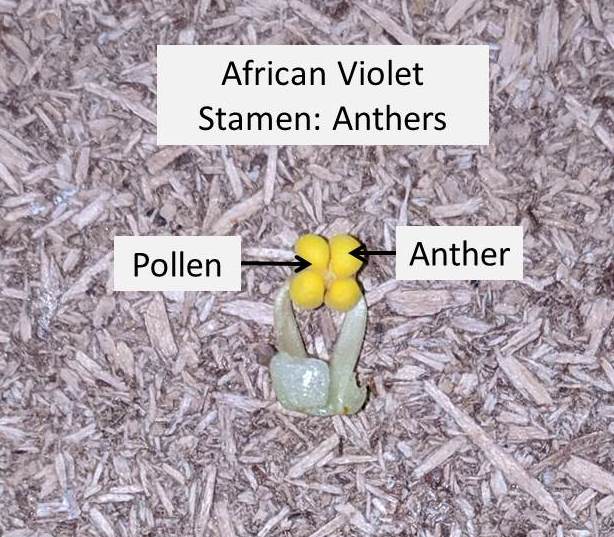
- Anther: Anthers are the oblong yellow sacs which form the tip of the stamen and are situated above the filament.
- The anthers or yellow sacs, contain pollen, which a fine powdery substance.
- This pollen contains the male reproductive cells.
- Filament: Filaments are the long fine structure forming the bottom part of the stamen. The filament holds the anther in place above it.

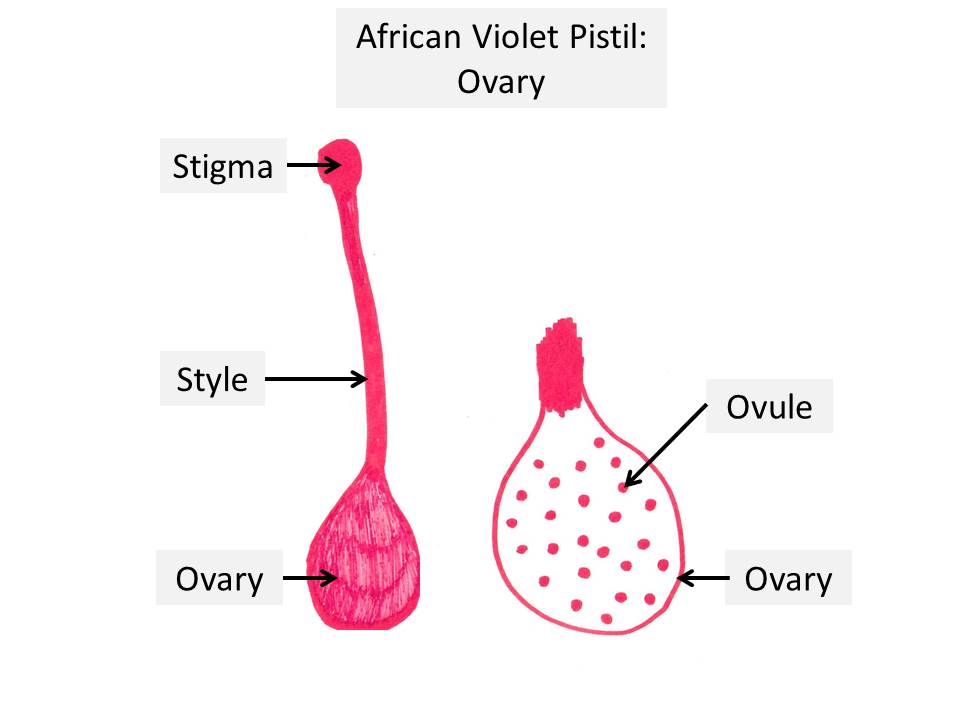
3. Pistil:
- Pistil is the female reproductive part of the flower.
- Pistil is also known as the carpel.
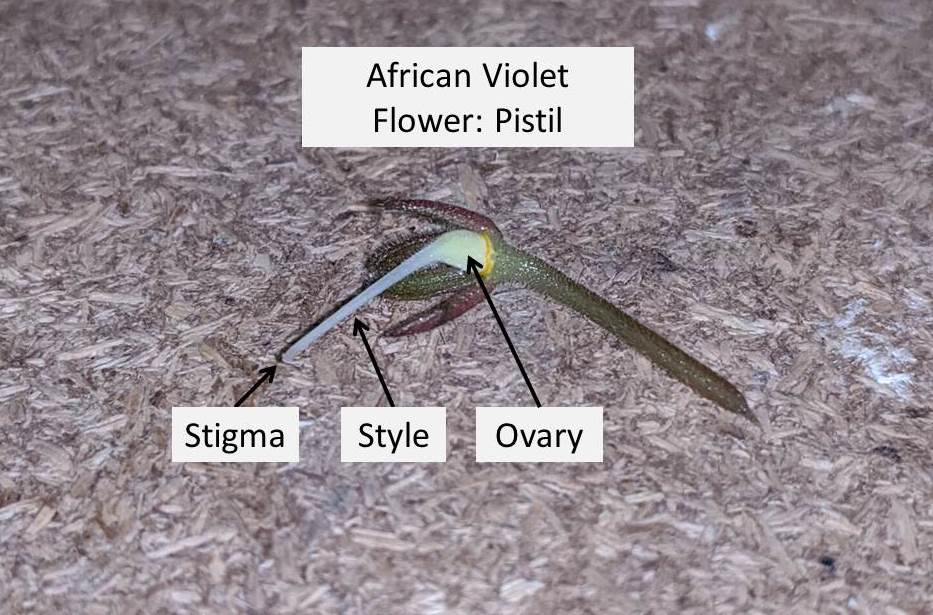
- Pistil is made up of three parts, the stigma, style and ovary.
- Within the pistil, the stigma is the uppermost tip, the style is the long tube, the ovary forms the bottom part of pistil.
- Stigma: Stigma forms the sticky tip of the pistil. It is responsible to receive the pollen (male reproductive tissue) and transport it down into the style.
- Style: Style is located immediately below the stigma. Style is long, thin and has a tube like structure. It is responsible to support and position the stigma to receive pollen. The pollen travels from the stigma through the style into the ovary.
- Ovary: Ovary is located below the style and forms the base of the pistil. Ovary supports both the style and stigma above. Ovary contains ovules which are the female reproductive cells or eggs. When the pollen travels from the stigma, through the style and reaches the ovary, it fertilizes the ovules eventually to form seed.


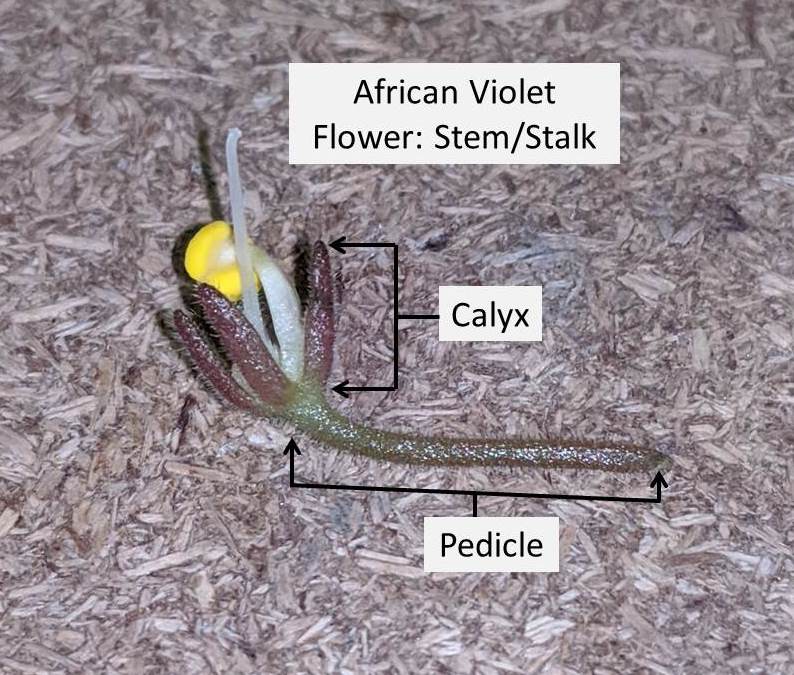
4. Stem:
- The stem of the flower is located at the base of the flower.
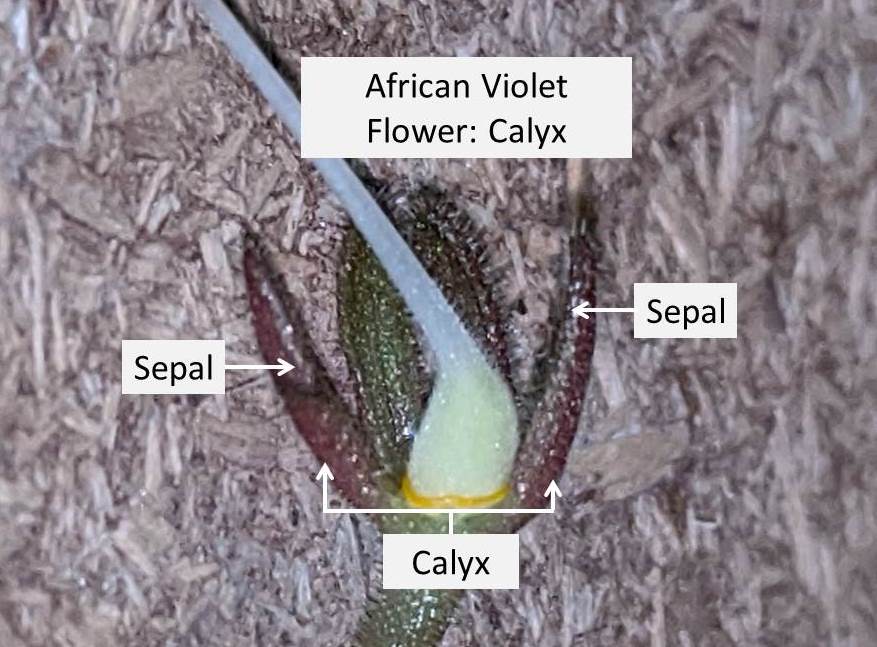
- Stem consists of two parts, calyx and pedicle.
- Calyx: Calyx forms a cup like structure, supporting the base of the flower. Calyx consists of small leaf/petal like structures known as Sepals. The sepals cradle the flower within it and hold the reproductive organs in place.
- Pedicle: Pedicle is located below the calyx and is a thin long filament like structure. Pedicle supports the calyx and holds the flower structure in place.
African Violet Leaf:
- African Violet leaves can be of different types, depending upon the margin features. These include, plain, quilted, spooned, wavy etc… For more details on African Violet leaf types, can visit my blog post, “What are the Different Leaf Types of African Violet Plants?”
- However, the basic structure of all African Violet leaves remains the same.






Parts Of An African Violet Leaf:
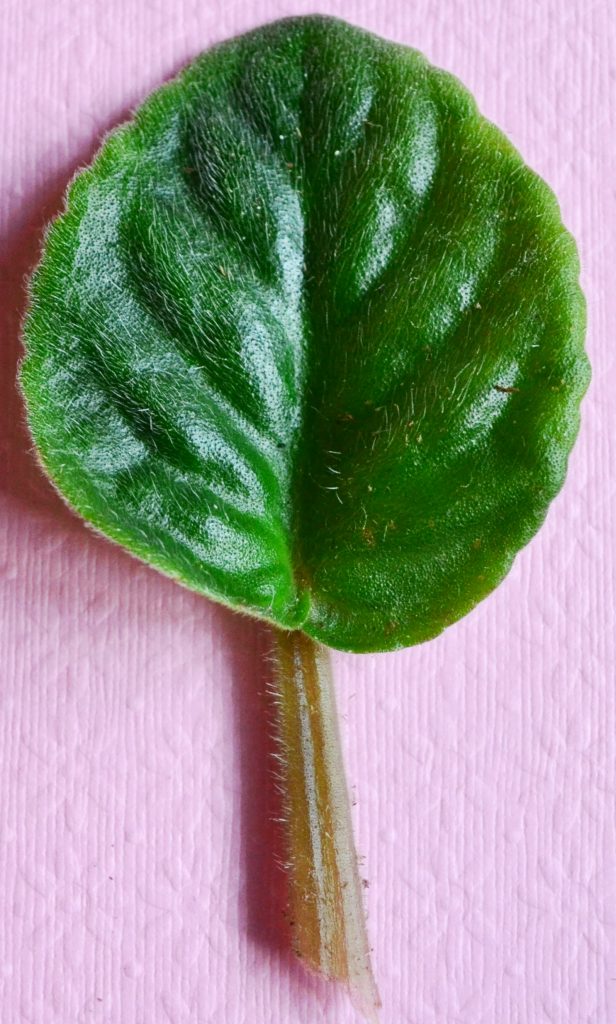
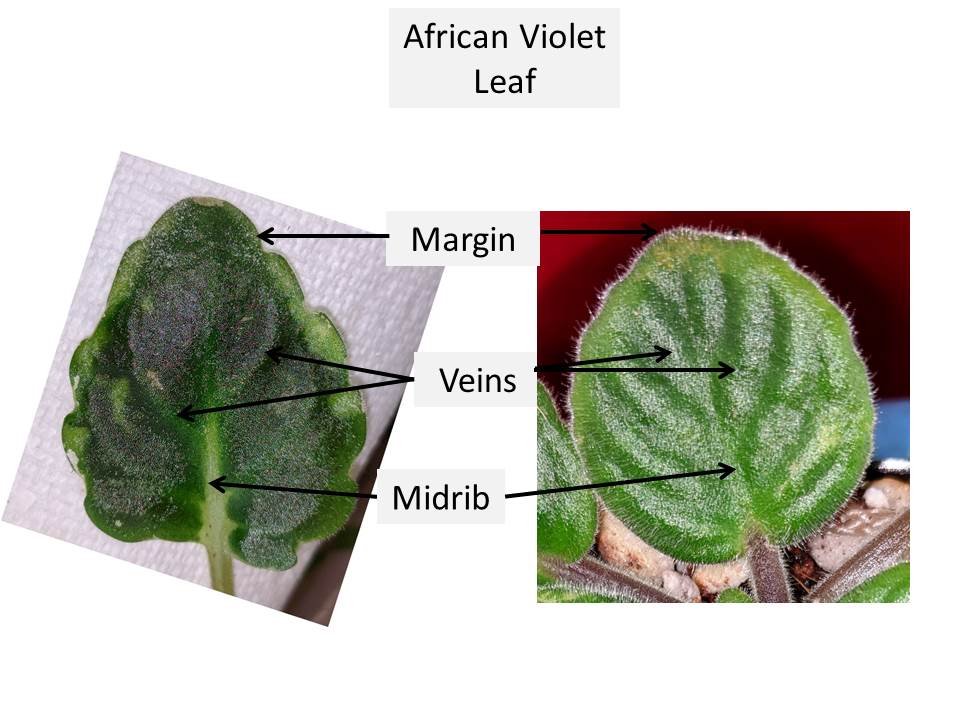
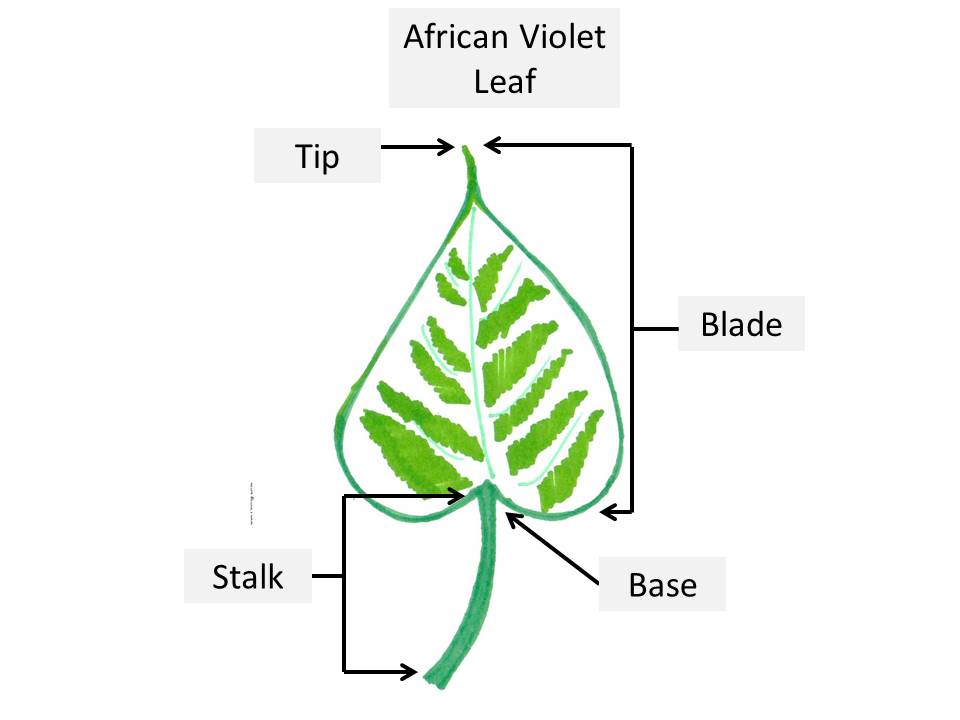
- African Violet leaf can be divided into two parts the blade and the stalk.
- The blade forms the large surface area of the leaf responsible for absorbing sunlight.
- The stalk originates at the base of the blade. Stalk holds the blade upright.
- The function of the stalk is to transport nutrients and water absorbed from the roots to the leaf.
- It also transports energy absorbed by the blade to the rest of the African Violet plant.
- Blade: The blade consists of the tip and the base.
- The outer outline of the leaf is known as the margin.
- In the center of the blade, runs a thick fleshy structure from the base to the tip known as the midrib.
- From the midrib, thin vein like structures arise, known as veins.

Examples of 2″ & 3″plastic pots, great to keep a few extra in your growing tools:

*Our Affiliate Programs: We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites. Though we do link to many items on Amazon out of convenience to our readers, we do also participate in other affiliate programs that also pay us a commission for any purchases you might make through our links (at no additional cost to you!).
Like this article?
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on Linkdin
Share on Pinterest


14 Responses
What is the Anther part good for ? Is it a seed ?
Hello,
thank you for your question. The anther contains the pollen sacs. Its the yellow powdery substance is the pollen. Its not a seed. Its the part that attaches to the stigma, where the seed is formed in the ovary. Hope this helps,
regards,
BV
Do the tiny leaves on the bloom stalk have a name? I’m not referring to the calyx. Thanks
Hello Sue, thank you for your question. Yes the tiny leaves on the bloom talk are known as “leaflets”. The main stem of the flower is called a “peduncle”. From this peduncle, the bloom stalk (which holds the flower) will branch off. Its on this bloom stalk that the tiny leaves appear. The leaves appear just slightly above the junction (joining point) where the bloom stalk meets the peduncle. Hope this makes sense. Maybe I can include a diagram in one of my posts.
regards,
Bv
Can not thank you enough for this clear, concise info! Ive been searching for such to share with fellow AV lovers in a FB group I’m in.
Again, thank you!
Thank you Cathy for your kind words, regards, BV
My violet has started to bloom again but only one of the 3 flowers that have opened so far have anthers, the others do not! Is this normal?
Hello N, thank you for your question. Yes this is normal, sometimes the flowers will not have anthers. I did hear about a new Optimara line of african violet plants which were anthereless and the anthers were omitted to prevent the transmission of flower bugs like thrips. Hope this helps,
BV
Hi. My violet blooms did not develop well, they dried up while very small (next time I will water more abundantly)… Once very shrivelled and dry, I cleaned up with tweezers and gently pulled each dried flower stem from their common base. That left the common base visible, looking dry itself, with very small holes. By the next day I noticed the two newish small upright leaves to be loose at that same flower stem base and have since half wilted. My Q’s are two…. 1) What is the name of the base from where the flower stems grow out of? and…. 2) How is it the two leaves were compromised by (I assume) my action? Thank you! : D
Hello Linda,
thank you for your question. I think the base from where the flower stem originates is called a node. Its the area between 2 leaves. It maybe that while you were trying to remove the flower stem using the tweezers, it sliced the neighboring leaves slightly too. That happens sometimes, the plant should recover and other surrounding leaves will take over that empty space soon. Hope this helps, BV
Are stems and stalks the same thing? I get confused about the various parts of an AV. I am searching for a diagram of ALL the parts of an AV, from top to bottom (under soil). And what is “pinching?” Seems to be better to cut a flower off? A place we should “pinch” would be good to show on the diagram. I know so little!
Hello Susan,
thank you for your question. The stalk is the main trunk of the plant. This is the long part from which the roots grow out of. Stalk can be interchangeably used with plant stem too. If it says plant stem then it refers to the plant stalk. However, if it says leaf stem or flower stem then it refers to the small thin green part which is underneath or connected to the leaf or flower. If you pinched off the flowers and are left with the long stem or stalk, you are welcome to remove those too. When removing the flowers the stem part should also be removed from the base of where it is attached to the stalk of the whole plant. Yes you are correct, you should remove the entire stem. New flowers, along with new stems will grow from the main stalk/trunk of the plant. New flowers will not grow again off that same stalk/stem, they need to be removed. When they say pinching, it refers to removing the flowers from the base of its stem, that is completely removing the flower+stem from its base. Hope this makes sense. I like your idea of having a diagram showing where exactly to pinch or remove the flowers. Will keep that in mind. regards,BV
What is the difference between a stem and a stalk? I am trying to read instructions for taking care of and pruning AVs, but the terminology confuses me. I am NEW to this process, haven’t had an AV for about 40 years. I have a tiny one that bloomed profusely, flowers died, I did pinch them off with fingers, that left a long “stem” or “stalk” which I am not sure of. So do new flowers grow off that same stem/stalk? So I pinch flowers right underneath each one, not down the stem/stalk? Or remove the entire stem/stalk? I guess I can do it various ways and see what happens!
Hello Susan,
thank you for your question. The stalk is the main trunk of the plant. This is the long part from which the roots grow out of. Stalk can be interchangeably used with plant stem too. If it says plant stem then it refers to the plant stalk. However, if it says leaf stem or flower stem then it refers to the small thin green part which is underneath or connected to the leaf or flower. If you pinched off the flowers and are left with the long stem or stalk, you are welcome to remove those too. When removing the flowers the stem part should also be removed from the base of where it is attached to the stalk of the whole plant. Yes you are correct, you should remove the entire stem. New flowers, along with new stems will grow from the main stalk/trunk of the plant. New flowers will not grow again off that same stalk/stem, they need to be removed. When they say pinching, it refers to removing the flowers from the base of its stem, that is completely removing the flower+stem from its base. Hope this makes sense. I like your idea of having a diagram showing where exactly to pinch or remove the flowers. Will keep that in mind. regards,BV